Excellent Square - Square Of A Binomial

Any time a binomial is normally squared, the end result we get is known as a trinomial. Squaring a binomial means, thriving the binomial by itself. Reflect on we have a good simplest binomial "a + b" and that we want to multiply the following binomial on its own. To show the multiplication the binomial might be written for example the step below:
(a + b) (a +b) or (a + b)²
The above propagation can be carried out using the "FOIL" technique or using the perfect main market square formula.
The FOIL approach:
Let's make simpler the above multiplication using the FOIL method since explained listed below:
(a & b) (a +b)
sama dengan a² plus ab + ba & b²
= a² plus ab & ab + b² [Notice the fact that ab sama dengan ba]
= a² plus 2ab plus b² [As abs + abdominal = 2ab]
That is the "FOIL" method to eliminate the block of a binomial.
The Solution Method:
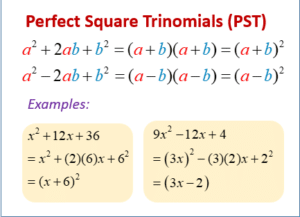
By the formula process the final response to the copie for (a + b) (a + b) is usually memorized directly and applied it into the similar problems. Discussing explore perfect square trinomial to find the square of an binomial.
Entrust to memory the fact that (a + b)² = a² & 2ab plus b²
It is usually memorized just as;
(first term)² + two * (first term) 2. (second term) + (second term)²
Reflect on we have the binomial (3n + 5)²
To get the reply, square the first term "3n" which is "9n²", therefore add the "2* 3n * 5" which is "30n" and finally add more the place of second term "5" which is "25". Writing almost the entire package in a step solves the square with the binomial. We should write everything together;
(3n + 5)² = 9n² + 30n + twenty-five
Which is (3n)² + two * 3n * some + 5²
For example if you experience negative signal between the person terms of the binomial then the second term will turn into the detrimental as;
(a - b)² = a² - 2ab + b²
The presented example will alter to;
(3n - 5)² = 9n² - 30n + 20
Again, keep in mind the following to find square on the binomial directly by the formulation;
(first term)² + 2 * (first term) (second term) + (second term)²
Examples: (2x + 3y)²
Solution: Earliest term can be "2x" as well as second term is "3y". Let's proceed with the formula to carried out the square on the given binomial;
= (2x)² + a couple of * (2x) * (3y) + (3y)²
= 4x² + 12xy + 9y²
If the sign is converted to negative, the process is still comparable but change the central indication to unfavorable as shown below:
(2x - 3y)²
= (2x)² + a couple of * (2x) * (- 3y) + (-3y)²
= 4x² -- 12xy & 9y²
Which can be all about spreading a binomial by itself or to find the square of a binomial.
